ICYMI, OpenClinica’s EHR-to-EDC solution, Unite™, is the technology backbone of the case study presented at the 5th Annual CERSI Innovations in Regulatory Science Summit.
CERSI, the UCSF-Stanford Center of Excellence in Regulatory Science and Innovation, is a “joint effort among members of a world-class team of highly collaborative scientists at University of California – San Francisco, Stanford University and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).” Each year, CERSI hosts an annual summit. More than 350 attendees gathered for the 2024 event, UCSF-Stanford CERSI’s largest in-person meeting ever.
The organizers of the 2024 annual summit invited 30 abstract submissions to be presented at in-person poster sessions. OpenClinica is proud to be featured alongside our collaborators, Adam Ansare of UCSF and Quantum Leap Healthcare Collaborative, Lynsey Bentley and Mitra Rocca of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, Food and Drug Administration, and Andrew Robinson, Kathleen Liu, Heidi Collins and Laura Esserman of UCSF.
EHR to EDC: OpenClinica Unite
If you are an avid reader of the OpenClinica blog, you are likely familiar with our eSource solution, Unite™ (originally called OneSource when it was first deployed in an active study in 2021). Clinical trial sponsors choose our EHR-to-EDC technology to accelerate their study timeline. They do this by eliminating the expense of errors associated with manual abstraction of electronic health record (EHR) data into clinical trial research databases (EDCs) and electronic case report forms (eCRFs). Unite eliminates manual data abstraction through a flexible integration framework, is launched directly within the patient’s EHR patient chart and automatically populates the exact data required by the trial protocol into eCRFs.
EHR to EDC: Proof Points
Our CERSI poster, OneSource: Automated EHR to eCRF Data Capture in Regulatory-Grade Clinical Trials, details how OpenClinica’s EHR-to-EDC technology was deployed in the “multicenter I-SPY COVID platform trial with over 3,200 patients including a Real World Data (RWD) observational cohort.”
The poster illustrates the SMART on FHIR integration – that is, Substitutable Medical Applications, Reusable Technologies (SMART) on Health Level Seven (HL7) Fast Health Interoperability Resources (FHIR) – which “enables the high quality, efficient transfer of discrete data from the EHR to the study database system,” specifically source data capture of laboratory and concomitant medication data.
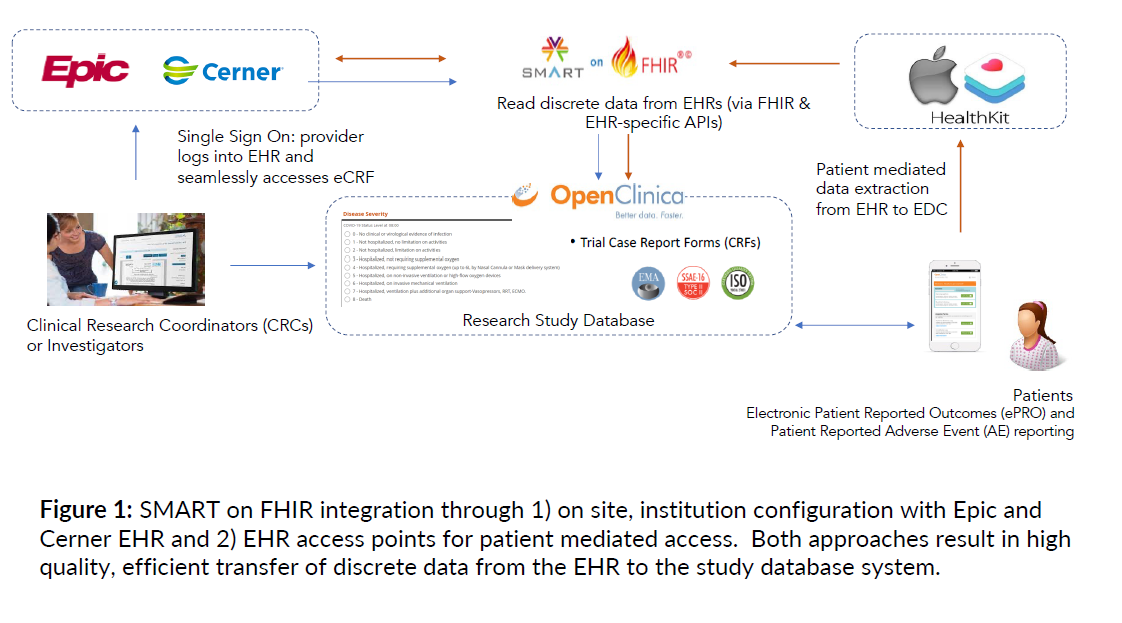
EHR to EDC: The Results
The results of EHR-to-EDC integration from this active I-SPY COVID study are compelling, dare I say extraordinary:
- 8,099 eCRFs from 878 subjects were evaluated for data entry quality.
- Using Unite (OneSource) automated capture, data entry times dropped to a median of 3.28 minutes, a decrease in data entry time by 45.8% (p<0.0001), a time savings of 2.8 minutes per form.
- Manual entry vs. EHR entered lab data for the same subject and lab results shows on average a discordance of 10.3%
- If every site had used Unite across site from trial startup, 2,300 hours saved for data entry alone.

Unite platform benefits compared to standard trial management.
As the poster states in the conclusion, Unite
EHR-to-EDC automated data capture resulted in a significant time savings, much improved data accuracy, sponsor-receipt of ‘real time’ data much more quickly, and better staff satisfaction,” as well as “the additional benefits of low implementation costs and reusability across sites compared to other EHR integration approaches.”
View the CERSI EHR to EDC poster here.

